让 F1C100s 从 SPI Nand 启动
目录
名词解释
| 名词 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| SPL | 第二阶段程序加载器 |
| BootROM | 固化在芯片内部的程序,用来识别并加载固件 |
写在前面
本次实验平台基于如下环境
| 名称 | 版本 |
|---|---|
| SoC | Allwinner Suniv F1C100s |
| u-boot | v2023.07 |
| linux | 6.4.0-rc4 |
| buildroot | v2023.02 |
| spi nand | Winbond W25N01G |
其实就是当时我从主线上master直接搞过来的,基本就是现在最新状态
如何从零构建一个完整的可从spi-nand启动的镜像?
可以说这是一份教程,也可以说是一次记录
启动流程
在正式开始之前,不妨先谈谈启动流程, 当然, 只是针对全志平台。
首先, 芯片内部的BootROM将spi-nand中的数据读取到SRAM中执行,但是为了兼容性(由于nand的page大小不同),BootROM只读取spi-nand中
每个page的前1024Bytes,这意味这你得对U-Boot SPL进行处理,将其分成按1K每Page的格式存放。
这得多亏了 bamkrs 提供的脚本 gen_sunxi_spinand_onlyboot_img.sh,你只需要输入page,erase block大小,就能让u-boot-sunxi-with-spl.bin中的SPL能够按BootROM需要的格式存放到flash中。好吧,有了这个东西,意味着从spi-nand启动变的可能。
我为了方便测试,所以通过sunxi-fel来烧录测试,
当你使用如上模式启动时,串口打印日志如下
U-Boot SPL 2023.07-rc4ninjar-lite-g1c30e10017-dirty (Jun 19 2023 - 08:33:14 -0400)
DRAM: 32 MiB
Unknown boot source from BROM: 0xe1a00000
Trying to boot from FEL
Trying to boot from XXX,定位到common/spl/spl.c + 712
static int boot_from_devices(struct spl_image_info *spl_image,
u32 spl_boot_list[], int count)
{
...
if (!CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(SILENT_CONSOLE)) {
if (loader)
printf("Trying to boot from %s\n",
spl_loader_name(loader));
...
if (loader &&
!spl_load_image(spl_image, loader)) {
spl_image->boot_device = bootdev;
return 0;
}
...
}
boot_from_devices 的调用者, 定位到common/spl/spl.c + 831
void board_init_r(gd_t *dummy1, ulong dummy2)
{
...
spl_image.boot_device = BOOT_DEVICE_NONE;
board_boot_order(spl_boot_list);
ret = boot_from_devices(&spl_image, spl_boot_list,
ARRAY_SIZE(spl_boot_list));
...
}
board_boot_order获取到了一个boot list,这个函数的原型是
他又通过调用 spl_boot_device 来获取启动设备,将其放入list首位,也就是将要启动的设备。
我看过了,这个函数只是个声明,对于全志平台,是这么实现的,位于文件arch/arm/mach-sunxi/board.c中,
调用流程如下
我把相关的函数都放到下面了,你可以花点时间整理下思路
u32 spl_boot_device(void)
{
return sunxi_get_boot_device();
}
uint32_t sunxi_get_boot_device(void)
{
int boot_source = sunxi_get_boot_source();
switch (boot_source) {
case SUNXI_INVALID_BOOT_SOURCE:
return BOOT_DEVICE_BOARD;
case SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_MMC0:
case SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_MMC0_HIGH:
return BOOT_DEVICE_MMC1;
case SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_NAND:
return BOOT_DEVICE_NAND;
case SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_MMC2:
case SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_MMC2_HIGH:
return BOOT_DEVICE_MMC2;
case SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_SPI:
return BOOT_DEVICE_SPI;
}
panic("Unknown boot source %d\n", boot_source);
return -1; /* Never reached */
}
static int sunxi_get_boot_source(void)
{
struct boot_file_head *egon_head = (void *)SPL_ADDR;
struct toc0_main_info *toc0_info = (void *)SPL_ADDR;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MACH_SUNIV) &&
!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD))
return SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_MMC0;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MACH_SUNIV))
return suniv_get_boot_source();
if (sunxi_egon_valid(egon_head))
return readb(&egon_head->boot_media);
if (sunxi_toc0_valid(toc0_info))
return readb(&toc0_info->platform[0]);
/* Not a valid image, so we must have been booted via FEL. */
return SUNXI_INVALID_BOOT_SOURCE;
}
static int suniv_get_boot_source(void)
{
/* Get the last function call from BootROM's stack. */
u32 brom_call = *(u32 *)(uintptr_t)(fel_stash.sp - 4);
/* translate SUNIV BootROM stack to standard SUNXI boot sources */
switch (brom_call) {
case SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_MMC0:
return SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_MMC0;
case SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_SPI:
return SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_SPI;
case SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_MMC1:
return SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_MMC2;
/* SPI NAND is not supported yet. */
case SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_NAND:
return SUNXI_INVALID_BOOT_SOURCE;
}
/* If we get here something went wrong try to boot from FEL.*/
printf("Unknown boot source from BROM: 0x%x\n", brom_call);
return SUNXI_INVALID_BOOT_SOURCE;
}
SPL_LOAD_IMAGE_METHOD来添加一个spl loader,而前面的函数boot_from_devices里就会比对这个数值,选择相应的spl loader,这个宏的原型如下
#define SPL_LOAD_IMAGE_METHOD(_name, _priority, _boot_device, _method) \
SPL_LOAD_IMAGE(_boot_device ## _priority ## _method) = { \
.name = _name, \
.boot_device = _boot_device, \
.load_image = _method, \
}
struct spl_image_loader {
#ifdef CONFIG_SPL_LIBCOMMON_SUPPORT
const char *name;
#endif
uint boot_device;
/**
* load_image() - Load an SPL image
*
* @spl_image: place to put image information
* @bootdev: describes the boot device to load from
*/
int (*load_image)(struct spl_image_info *spl_image,
struct spl_boot_device *bootdev);
};
我们先找一个现有的例子看看该结构体如下
static int spl_board_load_image(struct spl_image_info *spl_image,
struct spl_boot_device *bootdev)
{
debug("Returning to FEL sp=%x, lr=%x\n", fel_stash.sp, fel_stash.lr);
return_to_fel(fel_stash.sp, fel_stash.lr);
return 0;
}
SPL_LOAD_IMAGE_METHOD("FEL", 0, BOOT_DEVICE_BOARD, spl_board_load_image);
可以看到,1. 名字 2. 优先级 3.启动源 4. 启动函数,原来上面spl_image_loader结构体里boot_device成员里存放的就是这个宏传入的启动源。 我们可以试着写一个从spi-nand启动的宏了,但东西都还没有实现,当然了!
看到这里我们大概了解了,怎么去实现一个自定义的spl loader了。本文章的实现章节会有相应细节,我们继续看往下流程。
所以我假设你已经实现了从spi-nand启动的loader,接着往下看。boot_from_devices调用完成以后,经过一堆东西,来到函数board_init_r最底下
spl_board_prepare_for_boot是一个声明,可以让你实现跳转u-boot前所做的最后工作。
jump_to_image_no_args 就是跳转到u-boot入口的函数了,实现如下
__weak void __noreturn jump_to_image_no_args(struct spl_image_info *spl_image)
{
typedef void __noreturn (*image_entry_noargs_t)(void);
image_entry_noargs_t image_entry =
(image_entry_noargs_t)spl_image->entry_point;
debug("image entry point: 0x%lx\n", spl_image->entry_point);
image_entry();
}
spl_image中解析出的entry_point,通过直接调用这个指针,就跳转到了u-boot中,这个entry_point是通过解析u-boot头部得到的,这个头部结构体是legacy_img_hdr,定义如下
#define IH_NMLEN 32 /* Image Name Length */
struct legacy_img_hdr {
uint32_t ih_magic; /* Image Header Magic Number */
uint32_t ih_hcrc; /* Image Header CRC Checksum */
uint32_t ih_time; /* Image Creation Timestamp */
uint32_t ih_size; /* Image Data Size */
uint32_t ih_load; /* Data Load Address */
uint32_t ih_ep; /* Entry Point Address */
uint32_t ih_dcrc; /* Image Data CRC Checksum */
uint8_t ih_os; /* Operating System */
uint8_t ih_arch; /* CPU architecture */
uint8_t ih_type; /* Image Type */
uint8_t ih_comp; /* Compression Type */
uint8_t ih_name[IH_NMLEN]; /* Image Name */
};
hexdump工具查看u-boot.img头部,得到如下信息
00000000 27 05 19 56 9b b7 3b c2 64 9e 77 80 00 06 06 c0 |'..V..;.d.w.....|
00000010 81 70 00 00 81 70 00 00 b6 2e 5e 67 11 02 05 00 |.p...p....^g....|
00000020 55 2d 42 6f 6f 74 20 32 30 32 33 2e 30 37 2d 72 |U-Boot 2023.07-r|
00000030 63 34 6e 69 6e 6a 61 72 2d 6c 69 74 65 2d 67 61 |c4ninjar-lite-ga|
00000040 b8 00 00 ea 14 f0 9f e5 14 f0 9f e5 14 f0 9f e5 |................|
00000050 14 f0 9f e5 14 f0 9f e5 14 f0 9f e5 14 f0 9f e5 |................|
u-boot.bin头部,我们得知,从 0x00 开始到 0x40 结束的 64字节,就是所谓的legacy image header,也就是上面结构体struct legacy_img_hdr中的内容, 我们将其从flash中读到内存中,定义个指针指向他就好了。在本案例中,ih_load,ih_ep皆为 0x81700000
所以,真相大白于天下了,看起来也没那么难,是吧
实现
我建议看看我在 ninjar-bsp 中对 u-boot 的这两次 commit,比较直观, 但我也会在下面讲实现过程 1. adding support for booting from spi-nand flash for sunxi. 2. f1c100s supportting boot from spi-nand from now !!!
第一个提交基本实现了调用到自己spl loader的路径
第二个提交实现了从spi-nand中读出header和u-boot
好,我们接下来讨论下实现,首先应该从全志的启动源入手,你应该没忘记吧,视线回到这个函数suniv_get_boot_source
struct fel_stash {
uint32_t sp;
uint32_t lr;
uint32_t cpsr;
uint32_t sctlr;
uint32_t vbar;
};
struct fel_stash fel_stash __section(".data");
static int suniv_get_boot_source(void)
{
/* Get the last function call from BootROM's stack. */
u32 brom_call = *(u32 *)(uintptr_t)(fel_stash.sp - 4);
/* translate SUNIV BootROM stack to standard SUNXI boot sources */
switch (brom_call) {
...
/* SPI NAND is not supported yet. */
case SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_NAND:
return SUNXI_INVALID_BOOT_SOURCE;
}
/* If we get here something went wrong try to boot from FEL.*/
printf("Unknown boot source from BROM: 0x%x\n", brom_call);
return SUNXI_INVALID_BOOT_SOURCE;
}
fel_stash.sp - 4的地方,得到了bootrom最后调用的函数,这真的太酷了!
可以看到SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_NAND分支直接返回了SUNXI_INVALID_BOOT_SOURCE表示无效启动源,所以我们需要改成下面这样
/* The low 8-bits of the 'boot_media' field in the SPL header */
#define SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_MMC0 0
#define SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_NAND 1
#define SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_MMC2 2
#define SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_SPI 3
#define SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_SPI_NAND 4
/*
* Values taken from the F1C200s BootROM stack
* to determine where we booted from.
*/
#define SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_MMC0 0xffff40f8
#define SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_NAND 0xffff4114
#define SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_SPI 0xffff4130
#define SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_MMC1 0xffff4150
#define SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_FEL 0xe1a00000
static int suniv_get_boot_source(void)
{
/* Get the last function call from BootROM's stack. */
u32 brom_call = *(u32 *)(uintptr_t)(fel_stash.sp - 4);
/* translate SUNIV BootROM stack to standard SUNXI boot sources */
switch (brom_call) {
...
/* SPI NAND is not supported yet. */
case SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_FEL:
case SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_NAND:
return SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_SPI_NAND;
}
/* If we get here something went wrong try to boot from FEL.*/
printf("Unknown boot source from BROM: 0x%x\n", brom_call);
return SUNXI_INVALID_BOOT_SOURCE;
}
spl loader那里。测试完了后面要删掉,不然影响你原来的FEL loader
宏SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_SPI_NAND,SUNIV_BOOTED_FROM_FEL位于arch/arm/include/asm/arch-sunxi/spl.h中
之前从 FEL 启动日志里看到会打印从FEL启动的函数地址 0xe1a00000,所以顺手加上了
U-Boot SPL 2023.07-rc4ninjar-lite-g1c30e10017-dirty (Jun 19 2023 - 08:33:14 -0400)
DRAM: 32 MiB
Unknown boot source from BROM: 0xe1a00000
Trying to boot from FEL
接下来就是修改函数sunxi_get_boot_device,在其中添加对SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_SPI_NAND的识别,让其返回BOOT_DEVICE_NAND
uint32_t sunxi_get_boot_device(void)
{
int boot_source = sunxi_get_boot_source();
switch (boot_source) {
...
case SUNXI_BOOTED_FROM_SPI_NAND:
return BOOT_DEVICE_NAND;
}
panic("Unknown boot source %d\n", boot_source);
return -1; /* Never reached */
}
很好,启动源转换的部分已经做完了,接下来就是添加一个针对spi-nand的spl loader了
我们在arch/arm/mach-sunxi下新建一个文件spl_spi_nand_sunxi.c
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0+
/*
* Copyright (C) 2023 iotah <writeforever@foxmail.com>
*/
#include <common.h>
#include <image.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <log.h>
#include <spl.h>
#include <hang.h>
#include <asm/arch/spl.h>
#include <asm/gpio.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <linux/bitops.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/libfdt.h>
#ifdef CONFIG_SPL_OS_BOOT
#error CONFIG_SPL_OS_BOOT is not supported yet
#endif
/*****************************************************************************/
/* SUN4I variant of the SPI controller */
/*****************************************************************************/
#define SUN4I_SPI0_CCTL 0x1C
#define SUN4I_SPI0_CTL 0x08
#define SUN4I_SPI0_RX 0x00
#define SUN4I_SPI0_TX 0x04
#define SUN4I_SPI0_FIFO_STA 0x28
#define SUN4I_SPI0_BC 0x20
#define SUN4I_SPI0_TC 0x24
#define SUN4I_CTL_ENABLE BIT(0)
#define SUN4I_CTL_MASTER BIT(1)
#define SUN4I_CTL_TF_RST BIT(8)
#define SUN4I_CTL_RF_RST BIT(9)
#define SUN4I_CTL_XCH BIT(10)
/*****************************************************************************/
/* SUN6I variant of the SPI controller */
/*****************************************************************************/
#define SUN6I_SPI0_CCTL 0x24
#define SUN6I_SPI0_GCR 0x04
#define SUN6I_SPI0_TCR 0x08
#define SUN6I_SPI0_FIFO_STA 0x1C
#define SUN6I_SPI0_MBC 0x30
#define SUN6I_SPI0_MTC 0x34
#define SUN6I_SPI0_BCC 0x38
#define SUN6I_SPI0_TXD 0x200
#define SUN6I_SPI0_RXD 0x300
#define SUN6I_CTL_ENABLE BIT(0)
#define SUN6I_CTL_MASTER BIT(1)
#define SUN6I_CTL_SRST BIT(31)
#define SUN6I_TCR_XCH BIT(31)
/*****************************************************************************/
#define CCM_AHB_GATING0 (0x01C20000 + 0x60)
#define CCM_H6_SPI_BGR_REG (0x03001000 + 0x96c)
#ifdef CONFIG_SUN50I_GEN_H6
#define CCM_SPI0_CLK (0x03001000 + 0x940)
#else
#define CCM_SPI0_CLK (0x01C20000 + 0xA0)
#endif
#define SUN6I_BUS_SOFT_RST_REG0 (0x01C20000 + 0x2C0)
#define AHB_RESET_SPI0_SHIFT 20
#define AHB_GATE_OFFSET_SPI0 20
#define SPI0_CLK_DIV_BY_2 0x1000
#define SPI0_CLK_DIV_BY_4 0x1001
#define SPI0_CLK_DIV_BY_16 0x1007
#define SPI0_CLK_DIV_BY_32 0x100f
#define SPI0_CLK_DIV_BY_64 0x600
#define SPI_READ_MAX_SIZE 64 /* FIFO size, minus 4 bytes of the header */
struct sunxi_spi_reg_offsets {
ulong spi_ctl_reg;
ulong spi_ctl_xch_bitmask;
ulong spi_fifo_reg;
ulong spi_tx_reg;
ulong spi_rx_reg;
ulong spi_bc_reg;
ulong spi_tc_reg;
ulong spi_bcc_reg;
};
struct sunxi_spi_reg_offsets sun6i_spi_reg_offsets = {
.spi_ctl_reg = SUN6I_SPI0_TCR,
.spi_fifo_reg = SUN6I_SPI0_FIFO_STA,
.spi_tx_reg = SUN6I_SPI0_TXD,
.spi_rx_reg = SUN6I_SPI0_RXD,
.spi_bc_reg = SUN6I_SPI0_MBC,
.spi_tc_reg = SUN6I_SPI0_MTC,
.spi_bcc_reg = SUN6I_SPI0_BCC,
};
struct sunxi_spi_reg_offsets sun4i_spi_reg_offsets = {
.spi_ctl_reg = SUN4I_SPI0_CTL,
.spi_fifo_reg = SUN4I_SPI0_FIFO_STA,
.spi_tx_reg = SUN4I_SPI0_TX,
.spi_rx_reg = SUN4I_SPI0_RX,
.spi_bc_reg = SUN4I_SPI0_BC,
.spi_tc_reg = SUN4I_SPI0_TC,
.spi_bcc_reg = 0,
};
#define to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, reg) \
(spi->base + spi->reg_offsets->spi_##reg)
struct spi_nand_device {
char *name;
unsigned page;
size_t page_size;
size_t block_size;
};
struct sunxi_spi {
uintptr_t base;
size_t fifo_depth;
bool is_sun6i;
struct sunxi_spi_reg_offsets *reg_offsets;
ulong spi_ctl_xch_bitmask;
struct spi_nand_device nand_dev;
};
/*****************************************************************************/
/* Winbond SPI NAND Instructions Table */
/*****************************************************************************/
#define SPI_NAND_RESET 0xff /* device reset */
#define SPI_NAND_RD_ID 0x9f /* read jedec id */
#define SPI_NAND_RD_STAT_REG 0x0f /* read status register */
#define SPI_NAND_WD_STAT_REG 0x1f /* write status register */
#define SPI_NAND_WD_ON 0x06 /* write enable */
#define SPI_NAND_WD_OFF 0x04 /* write disable */
#define SPI_NAND_RD_PAGE_DATA 0x13 /* read page into data buffer */
#define SPI_NAND_RD_DATA 0x03 /* read from data buffer */
/*****************************************************************************/
static int __maybe_unused hexdump(ulong addr, uint32_t offset, int dump_len)
{
uint8_t *ptr = (uint8_t *)(addr + offset);
int data_per_line = 16;
for (int i = 0; i < dump_len; i++) {
if (i != 0 && i % data_per_line == 0) {
printf("\n");
}
if (i % data_per_line == 0) {
printf("%08x", (uint32_t)(addr + offset));
offset += sizeof(*ptr) * data_per_line;
}
if (i % 8)
printf(" %02x", *ptr++);
else
printf(" %02x", *ptr++);
}
puts("\n");
return 0;
}
/*
* Allwinner A10/A20 SoCs were using pins PC0,PC1,PC2,PC23 for booting
* from SPI Flash, everything else is using pins PC0,PC1,PC2,PC3.
* The H6 uses PC0, PC2, PC3, PC5, the H616 PC0, PC2, PC3, PC4.
*/
static void spi0_pinmux_setup(unsigned int pin_function)
{
/* All chips use PC0 and PC2. */
sunxi_gpio_set_cfgpin(SUNXI_GPC(0), pin_function);
sunxi_gpio_set_cfgpin(SUNXI_GPC(2), pin_function);
/* All chips except H6 and H616 use PC1. */
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SUN50I_GEN_H6))
sunxi_gpio_set_cfgpin(SUNXI_GPC(1), pin_function);
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MACH_SUN50I_H6))
sunxi_gpio_set_cfgpin(SUNXI_GPC(5), pin_function);
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MACH_SUN50I_H616))
sunxi_gpio_set_cfgpin(SUNXI_GPC(4), pin_function);
/* Older generations use PC23 for CS, newer ones use PC3. */
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MACH_SUN4I) || IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MACH_SUN7I) ||
IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MACH_SUN8I_R40))
sunxi_gpio_set_cfgpin(SUNXI_GPC(23), pin_function);
else
sunxi_gpio_set_cfgpin(SUNXI_GPC(3), pin_function);
}
static bool is_sun6i_gen_spi(void)
{
return IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SUNXI_GEN_SUN6I) ||
IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SUN50I_GEN_H6);
}
static uintptr_t spi0_base_address(void)
{
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MACH_SUN8I_R40))
return 0x01C05000;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SUN50I_GEN_H6))
return 0x05010000;
if (!is_sun6i_gen_spi() ||
IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MACH_SUNIV))
return 0x01C05000;
return 0x01C68000;
}
/*
* Setup 6 MHz from OSC24M (because the BROM is doing the same).
*/
static void spi0_enable_clock(void)
{
uintptr_t base = spi0_base_address();
/* Deassert SPI0 reset on SUN6I */
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SUN50I_GEN_H6))
setbits_le32(CCM_H6_SPI_BGR_REG, (1U << 16) | 0x1);
else if (is_sun6i_gen_spi())
setbits_le32(SUN6I_BUS_SOFT_RST_REG0,
(1 << AHB_RESET_SPI0_SHIFT));
/* Open the SPI0 gate */
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SUN50I_GEN_H6))
setbits_le32(CCM_AHB_GATING0, (1 << AHB_GATE_OFFSET_SPI0));
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MACH_SUNIV)) {
/* Divide by 32, clock source is AHB clock 200MHz */
writel(SPI0_CLK_DIV_BY_64, base + SUN6I_SPI0_CCTL);
} else {
/* Divide by 4 */
writel(SPI0_CLK_DIV_BY_4, base + (is_sun6i_gen_spi() ?
SUN6I_SPI0_CCTL : SUN4I_SPI0_CCTL));
/* 24MHz from OSC24M */
writel((1 << 31), CCM_SPI0_CLK);
}
if (is_sun6i_gen_spi()) {
/* Enable SPI in the master mode and do a soft reset */
setbits_le32(base + SUN6I_SPI0_GCR, SUN6I_CTL_MASTER |
SUN6I_CTL_ENABLE | SUN6I_CTL_SRST);
/* Wait for completion */
while (readl(base + SUN6I_SPI0_GCR) & SUN6I_CTL_SRST)
;
} else {
/* Enable SPI in the master mode and reset FIFO */
setbits_le32(base + SUN4I_SPI0_CTL, SUN4I_CTL_MASTER |
SUN4I_CTL_ENABLE |
SUN4I_CTL_TF_RST |
SUN4I_CTL_RF_RST);
}
}
static void spi0_disable_clock(void)
{
uintptr_t base = spi0_base_address();
/* Disable the SPI0 controller */
if (is_sun6i_gen_spi())
clrbits_le32(base + SUN6I_SPI0_GCR, SUN6I_CTL_MASTER |
SUN6I_CTL_ENABLE);
else
clrbits_le32(base + SUN4I_SPI0_CTL, SUN4I_CTL_MASTER |
SUN4I_CTL_ENABLE);
/* Disable the SPI0 clock */
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MACH_SUNIV))
writel(0, CCM_SPI0_CLK);
/* Close the SPI0 gate */
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SUN50I_GEN_H6))
clrbits_le32(CCM_AHB_GATING0, (1 << AHB_GATE_OFFSET_SPI0));
/* Assert SPI0 reset on SUN6I */
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SUN50I_GEN_H6))
clrbits_le32(CCM_H6_SPI_BGR_REG, (1U << 16) | 0x1);
else if (is_sun6i_gen_spi())
clrbits_le32(SUN6I_BUS_SOFT_RST_REG0,
(1 << AHB_RESET_SPI0_SHIFT));
}
static void spi0_init(struct sunxi_spi *spi)
{
unsigned int pin_function = SUNXI_GPC_SPI0;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MACH_SUN50I) ||
IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SUN50I_GEN_H6))
pin_function = SUN50I_GPC_SPI0;
else if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MACH_SUNIV))
pin_function = SUNIV_GPC_SPI0;
spi0_pinmux_setup(pin_function);
spi0_enable_clock();
spi->base = spi0_base_address();
spi->is_sun6i = is_sun6i_gen_spi();
spi->fifo_depth = SPI_READ_MAX_SIZE;
if (spi->is_sun6i) {
spi->reg_offsets = &sun6i_spi_reg_offsets;
spi->spi_ctl_xch_bitmask = SUN6I_TCR_XCH;
} else {
spi->reg_offsets = &sun4i_spi_reg_offsets;
spi->spi_ctl_xch_bitmask = SUN4I_CTL_XCH;
}
/* TODO: initialize SPI with specified mode */
}
static void spi0_deinit(struct sunxi_spi *spi)
{
/* New SoCs can disable pins, older could only set them as input */
unsigned int pin_function = SUNXI_GPIO_INPUT;
if (is_sun6i_gen_spi())
pin_function = SUNXI_GPIO_DISABLE;
spi0_disable_clock();
spi0_pinmux_setup(pin_function);
}
static ssize_t spi0_write_then_read(struct sunxi_spi *spi,
const void *txbuf, u32 n_tx,
void *rxbuf, u32 n_rx,
unsigned delay)
{
int i;
int timeout = 10;
unsigned real_delay = 200;
ssize_t len = 0;
ssize_t skip_bytes = 0;
u8 *txbuf8 = (u8 *)txbuf;
u8 *rxbuf8 = (u8 *)rxbuf;
ulong spi_bc_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, bc_reg);
ulong spi_tc_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, tc_reg);
ulong spi_bcc_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, bcc_reg);
ulong spi_rx_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, rx_reg);
ulong spi_tx_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, tx_reg);
ulong spi_ctl_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, ctl_reg);
ulong spi_fifo_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, fifo_reg);
if (delay > 0)
real_delay = delay;
/* Burst counter (total bytes) */
writel(n_tx + n_rx, spi_bc_reg);
/* Transfer counter (bytes to send) */
writel(n_tx, spi_tc_reg);
if (spi->is_sun6i)
writel(n_tx, spi_bcc_reg);
for (i = 0; i < n_tx; i++)
writeb((u8)txbuf8[i], spi_tx_reg);
/* Start the data transfer */
setbits_le32(spi_ctl_reg, spi->spi_ctl_xch_bitmask);
udelay(real_delay);
/* Wait until everything is received in the RX FIFO */
for (;;) {
if ((readl(spi_fifo_reg) & 0x0f) == (n_rx - 1))
break;
if (timeout-- < 0)
break;
}
/* Skip bytes */
for (skip_bytes = n_tx; skip_bytes--;)
readb(spi_rx_reg);
/* if only need to be write */
if (n_rx <= 0)
return 0;
while (n_rx-- > 0) {
len++;
*rxbuf8++ = readb(spi_rx_reg);
}
return (len == n_rx) ? -1 : len;
}
static inline u32 spi_nand_read_id(struct sunxi_spi *spi)
{
u8 cmds[] = {0x9f, 0x00};
u32 result;
ssize_t status;
status = spi0_write_then_read(spi, cmds, sizeof(cmds), &result, 3, 0);
result = cpu_to_be32(result) >> 8;
return (status < 0) ? status : result;
}
static inline u8
spi_nand_read_status_reg(struct sunxi_spi *spi, u8 reg_addr)
{
u8 result = {0};
u8 txbuf[] = { 0x0f, reg_addr };
ssize_t status;
status = spi0_write_then_read(spi, txbuf, sizeof(txbuf),
&result, sizeof(result), 0);
return (status < 0) ? status : result;
}
static inline ssize_t
spi_nand_write_status_reg(struct sunxi_spi *spi, u8 reg_addr, u8 reg_val)
{
u8 txbuf[] = { 0x1f, reg_addr, reg_val };
return spi0_write_then_read(spi, txbuf, sizeof(txbuf),
NULL, 0, 0);
}
static inline int spi_nand_init(struct sunxi_spi *spi)
{
puts("loading payload from SPI NAND ...\n");
u32 id = spi_nand_read_id(spi);
printf("detected JEDEC ID : 0x%08x\n", id);
if (id == 0x00efaa21) {
spi->nand_dev.name = "w25n01g";
spi->nand_dev.page_size = (1 << 11); /* 2048 */
spi->nand_dev.block_size = (1 << 17); /* 128KB */
} else {
puts("###### NAND Device Not supported yet! #####\n");
hang();
}
/* in the beginning, there's no page was loaded into cache */
spi->nand_dev.page = -1;
/* set spinand into continuous read mode */
u8 stat2 = spi_nand_read_status_reg(spi, 0xb0);
stat2 |= (1 << 4) | (1 << 3); /* bit BUF = 1, ECC-E = 1 */
spi_nand_write_status_reg(spi, 0xb0, stat2);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t
spi_nand_load_page_op(struct sunxi_spi *spi, unsigned page)
{
u8 txbuf[] = {
SPI_NAND_RD_PAGE_DATA,
0x00, /* dummy clock */
(u8)(page >> 8),
(u8)(page),
};
return spi0_write_then_read(spi, txbuf, sizeof(txbuf),
NULL, 0, 500);
}
static ssize_t
spi_nand_read_from_cache_op(struct sunxi_spi *spi, unsigned column,
void *rxbuf, size_t len)
{
u8 txbuf[] = {
SPI_NAND_RD_DATA,
(u8)(column >> 8),
(u8)(column),
0x00, /* dummy clock */
};
return spi0_write_then_read(spi, txbuf, sizeof(txbuf), rxbuf, len, 0);
}
static int sunxi_spi0_nand_read_data(struct sunxi_spi *spi, void *buf, u32 addr, u32 len)
{
ssize_t status;
unsigned page = addr >> 11;
/* load page to data buffer */
if (spi->nand_dev.page != page) {
spi->nand_dev.page = page;
spi_nand_load_page_op(spi, page);
}
/*
* the check the addr, make sure it's in data buffer
* usually be used to load the endless of the page
*/
addr &= 0x7FF;
if (len + addr > spi->nand_dev.page_size)
len = spi->nand_dev.page_size - addr;
status = spi_nand_read_from_cache_op(spi, addr, buf, len);
return status;
}
static int spi0_nand_read_data(struct sunxi_spi *spi, void *buf, u32 addr, u32 len)
{
u8 *buf8 = buf;
u32 chunk_len;
size_t loop_count = 0;
while (len > 0) {
chunk_len = len;
if (chunk_len > SPI_READ_MAX_SIZE)
chunk_len = SPI_READ_MAX_SIZE;
sunxi_spi0_nand_read_data(spi, buf8, addr, chunk_len);
len -= chunk_len;
buf8 += chunk_len;
addr += chunk_len;
loop_count++;
}
return 0;
}
static int spl_spi_nand_load_image(struct spl_image_info *spl_image,
struct spl_boot_device *bootdev)
{
int ret = 0;
struct legacy_img_hdr *header;
uint32_t load_offset = sunxi_get_spl_size();
header = (struct legacy_img_hdr *)CONFIG_TEXT_BASE;
load_offset = max_t(uint32_t, load_offset, CONFIG_SYS_SPI_U_BOOT_OFFS);
struct sunxi_spi *spi = (struct sunxi_spi *)malloc(sizeof(struct sunxi_spi));
spi0_init(spi);
spi_nand_init(spi);
spi0_nand_read_data(spi, (void *)header, load_offset, 0x40);
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SPL_LOAD_FIT) &&
image_get_magic(header) == FDT_MAGIC) {
debug("Not supported FIT image yet!\n");
} else {
ret = spl_parse_image_header(spl_image, bootdev, header);
if (ret)
return ret;
spi0_nand_read_data(spi, (void *)spl_image->load_addr,
load_offset, spl_image->size);
}
spi0_deinit(spi);
return ret;
}
/* Use priorty 0 to override the default if it happens to be linked in */
SPL_LOAD_IMAGE_METHOD("sunxi SPI-NAND", 0, BOOT_DEVICE_NAND, spl_spi_nand_load_image);
entry_point处的地址
有关读器件的细节,以及平台SPI的通信,我想应该没太多人感兴趣,也不是本文重点,所以放到文章末尾更多章节中吧
优化思路
所以这个启动流程还是有很多优化空间的,比如如下几个部分
- SPI的时钟。我只给了SPI 3MHz的速率,跟BootROM中的一致,所以你可以试着提高下这个速度,也许会读的更快
- uboot 设备树里 spi节点设置的速度,也会影响读flash的速度
- 程序里可能有些没必要的环节,可以优化掉
- 如果空间足够大,就不要压缩固件了,解压也会消耗掉一部分时间,但不会太多
- 暂时没想到,以后再说吧
基准测试
SPI速率
SPI的父时钟来自于200MHz的AHB总线,可通过调整分频系数来控制SPI控制器的主时钟
我们使用如下方法统计耗时
#define TIMER_CLOCK (24 * 1000 * 1000)
#define TICKS_PER_HZ (TIMER_CLOCK / CONFIG_SYS_HZ)
#define TICKS_TO_HZ(x) ((x) / TICKS_PER_HZ)
unsigned long ts = get_timer(0);
unsigned long te = get_timer(0);
printk("cost : %ld (tick), %ld (ms)", te - ts, TICKS_TO_HZ((te - ts) * 1000));
结论,SPI速率对spl加载uboot无太大影响,微乎其微。
更多
W25N01G的读操作流程
W25N01G normal 读模式下,需要先将page加载到器件内部data buffer,然后再发送读指令,从data buffer中获取数据。 然后加载下一页,反复。还有一种连续读方式,可以一次性读出整个page,但是这个片子的SPI RX FIFO没有那么大。
static ssize_t spi0_write_then_read(struct sunxi_spi *spi,
const void *txbuf, u32 n_tx,
void *rxbuf, u32 n_rx,
unsigned delay)
{
int i;
int timeout = 10;
unsigned real_delay = 200;
ssize_t len = 0;
ssize_t skip_bytes = 0;
u8 *txbuf8 = (u8 *)txbuf;
u8 *rxbuf8 = (u8 *)rxbuf;
ulong spi_bc_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, bc_reg);
ulong spi_tc_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, tc_reg);
ulong spi_bcc_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, bcc_reg);
ulong spi_rx_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, rx_reg);
ulong spi_tx_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, tx_reg);
ulong spi_ctl_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, ctl_reg);
ulong spi_fifo_reg = to_sunxi_spi_reg(spi, fifo_reg);
if (delay > 0)
real_delay = delay;
/* Burst counter (total bytes) */
writel(n_tx + n_rx, spi_bc_reg);
/* Transfer counter (bytes to send) */
writel(n_tx, spi_tc_reg);
if (spi->is_sun6i)
writel(n_tx, spi_bcc_reg);
for (i = 0; i < n_tx; i++)
writeb((u8)txbuf8[i], spi_tx_reg);
/* Start the data transfer */
setbits_le32(spi_ctl_reg, spi->spi_ctl_xch_bitmask);
udelay(real_delay);
/* Wait until everything is received in the RX FIFO */
for (;;) {
if ((readl(spi_fifo_reg) & 0x0f) == (n_rx - 1))
break;
if (timeout-- < 0)
break;
}
/* Skip bytes */
for (skip_bytes = n_tx; skip_bytes--;)
readb(spi_rx_reg);
/* if only need to be write */
if (n_rx <= 0)
return 0;
while (n_rx-- > 0) {
len++;
*rxbuf8++ = readb(spi_rx_reg);
}
return (len == n_rx) ? -1 : len;
}
static ssize_t
spi_nand_load_page_op(struct sunxi_spi *spi, unsigned page)
{
u8 txbuf[] = {
SPI_NAND_RD_PAGE_DATA,
0x00, /* dummy clock */
(u8)(page >> 8),
(u8)(page),
};
return spi0_write_then_read(spi, txbuf, sizeof(txbuf),
NULL, 0, 500);
}
static ssize_t
spi_nand_read_from_cache_op(struct sunxi_spi *spi, unsigned column,
void *rxbuf, size_t len)
{
u8 txbuf[] = {
SPI_NAND_RD_DATA,
(u8)(column >> 8),
(u8)(column),
0x00, /* dummy clock */
};
return spi0_write_then_read(spi, txbuf, sizeof(txbuf), rxbuf, len, 0);
}
全志 F1C100s SPI裸机通信的
第一步就是开时钟这些。比较关键的就是发送接收,下面是些寄存器相关的操作
SPI_MBC_REG (SPI Burst Counter Register)寄存器,里面存的是 (发 + 收)字节的总和
SPI_TCR_REG (SPI Transfer Control Register),这里面需要存入发送的字节数SPI_BCC_REG (SPI Burst Control Register), sun6i变体还要将发送字节数写入该寄存器
SPI_TXD_REG (SPI TX Data Register), 将要发送的字节依次写入该寄存器。数量不应超过fifo长度。
SPI_TCR_REG (SPI Transfer Control Register),通过置位该寄存器的第31位,触发传输流程
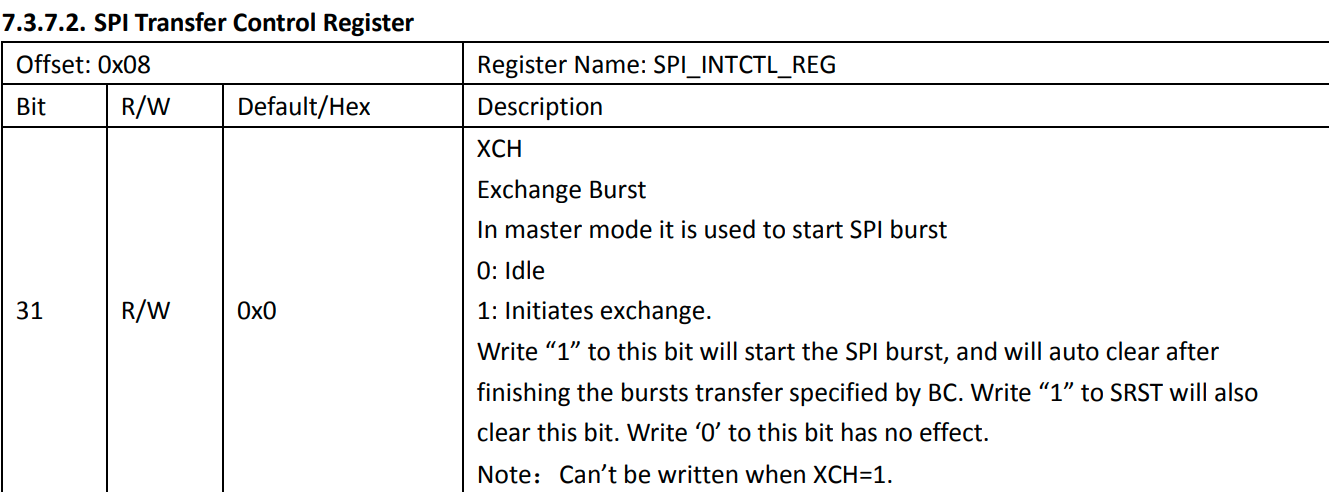
/* Start the data transfer */
setbits_le32(spi_ctl_reg, spi->spi_ctl_xch_bitmask);
udelay(real_delay);
SPI_FSR_REG (SPI FIFO Status Register),该寄存器低8位表示RX FIFO中接收的字节数,最大64 bytes
/* Wait until everything is received in the RX FIFO */
for (;;) {
if ((readl(spi_fifo_reg) & 0xff) == (n_rx - 1))
break;
if (timeout-- < 0)
break;
}
因为控制器内部原因,需要跳过一部分RX寄存器中的无效值。
参考资料
F1C100S-BOOTROM与SPL阶段 V3s SPI NAND u-boot @openwrt V3s/S3/f1c100s通过USB启动Linux,并把SD NAND/TF卡挂载为U盘, 可以dd或Win32DiskImager任烧写
